In modern manufacturing, performance is no longer defined merely by dimensional accuracy or material selection. Increasingly, it is the surface that determines how long a component lasts, how efficiently it performs, and how reliably it functions in demanding applications. Surface finishing and superfinishing have therefore evolved from being post-machining cosmetic processes to becoming critical engineering imperatives. Across automotive, aerospace, heavy engineering, railways, energy, and precision manufacturing sectors, surface integrity has emerged as a decisive factor influencing productivity, quality, and lifecycle costs.
Understanding Surface Integrity Beyond Roughness
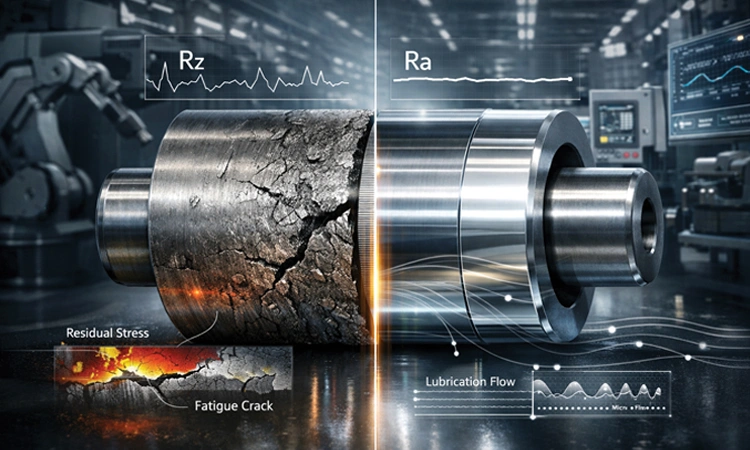
Traditionally, surface finish was evaluated primarily in terms of roughness values such as Ra or Rz. While these parameters remain important, today’s understanding of surface integrity is far more holistic. It encompasses not only surface topography, but also subsurface characteristics such as residual stresses, microhardness, grain deformation, and metallurgical alterations induced during machining or finishing.
Surface imperfections—microscopic peaks, valleys, burrs, or smeared material—can become initiation points for fatigue cracks, corrosion, and premature failure. In high-load or high-speed applications, even minor surface anomalies can lead to vibration, noise, heat generation, and reduced efficiency. Superfinishing processes address these challenges by refining surfaces at a micro and nano scale, ensuring optimal functional performance rather than mere visual smoothness.
Why Surface Finish Has Become a Manufacturing Imperative
The growing emphasis on surface and superfinishing is driven by multiple converging factors. First, machine tools and cutting technologies have advanced significantly, enabling higher speeds, feeds, and material removal rates. While this boosts productivity, it also increases the risk of surface damage if not followed by appropriate finishing.
Second, components today are expected to operate under far more severe conditions—higher pressures, temperatures, loads, and speeds—often for extended service intervals. Whether it is an automotive transmission gear, an aerospace bearing, a hydraulic spool valve, or a mould cavity, surface quality directly influences friction, wear, sealing, and lubrication behavior.
Third, sustainability and cost pressures demand longer component life, reduced downtime, and lower energy consumption. A well-finished surface reduces frictional losses, improves lubrication retention, and minimizes wear, thereby contributing to energy efficiency and reduced maintenance.
Superfinishing: From Enhancement to Enabler
Superfinishing processes such as honing, lapping, polishing, microfinishing, abrasive flow machining, mass finishing, and advanced abrasive belt finishing have transitioned from optional enhancements to essential enablers of performance.
In gear manufacturing, for instance, superfinishing significantly improves tooth flank geometry and surface texture, resulting in quieter operation, higher load-carrying capacity, and improved transmission efficiency. In bearing applications, superfinished raceways reduce rolling resistance, enhance fatigue life, and enable higher operating speeds.
Similarly, in hydraulic and pneumatic systems, superfinished surfaces ensure precise sealing, reduced leakage, and smoother actuation. In tooling and dies, superior surface finish enhances part release, reduces cycle times, and extends tool life.
Role of Surface Finish in Fatigue, Wear, and Reliability
Fatigue failure remains one of the most common causes of component breakdown, especially in dynamically loaded parts. Surface finish plays a critical role in fatigue performance because cracks almost always initiate at the surface. Rough surfaces amplify local stress concentrations, accelerating crack initiation.
Superfinishing reduces these stress risers by smoothing asperities and introducing beneficial compressive residual stresses. This dramatically improves fatigue life, sometimes by several multiples, particularly in rotating and cyclically loaded components such as shafts, gears, crankshafts, and camshafts.
Wear resistance is another area where surface finish is pivotal. A controlled surface texture ensures proper lubricant film formation and retention. Too smooth a surface may lead to lubricant starvation, while too rough a surface increases abrasion. Superfinishing allows manufacturers to engineer surfaces with the right balance of smoothness and texture, tailored to specific tribological requirements.
Precision Manufacturing and the Demand for Consistency
As manufacturing moves toward tighter tolerances and zero-defect expectations, consistency in surface quality becomes non-negotiable. Manual polishing and conventional finishing methods, while still relevant in certain applications, are increasingly being supplemented or replaced by automated and controlled superfinishing solutions.
Automation ensures repeatability, process stability, and traceability—key requirements in industries such as aerospace, defense, and medical devices. Advanced finishing machines now integrate closed-loop control, in-process measurement, and adaptive tooling to maintain consistent surface characteristics across batches.
Furthermore, digital manufacturing and Industry 4.0 initiatives are extending into surface finishing operations. Process data such as force, vibration, abrasive wear, and surface measurements are being monitored and analyzed to optimize outcomes and predict tool life.
Surface Finishing in Heavy Engineering and Infrastructure
In heavy engineering sectors—such as power generation, mining, railways, and steel—surface and superfinishing play a crucial role in ensuring robustness and longevity. Large shafts, rollers, turbine components, and rail parts operate under extreme loads and harsh environments.
Here, surface integrity is critical not only for performance but also for safety. Superfinishing helps mitigate risks such as surface-initiated fatigue cracks, corrosion fatigue, and fretting wear. With infrastructure assets expected to last decades, the upfront investment in superior surface finishing pays dividends through reduced failures and lifecycle costs.
Surface & Superfinishing in Automotive and Aerospace Applications
In the automotive and aerospace industries, surface and superfinishing are not merely quality enhancers but mission-critical enablers of performance, safety, and compliance. Automotive components such as engine parts, transmission gears, fuel injection systems, and EV drivetrain elements rely heavily on controlled surface textures to reduce friction, improve fuel or energy efficiency, lower NVH (noise, vibration, and harshness), and extend service life. In aerospace, where components operate under extreme stresses, temperatures, and cyclic loads, surface integrity directly influences fatigue resistance, crack initiation, and corrosion behavior. Superfinished surfaces in bearings, turbine components, landing gear, and structural parts contribute to higher reliability, weight reduction, and longer maintenance intervals—key imperatives in an industry governed by stringent certification standards and zero-failure tolerance. In both sectors, advanced superfinishing ensures consistency, repeatability, and traceability, aligning surface quality with the growing demands of electrification, lightweighting, and next-generation propulsion systems.
Sustainability and Resource Efficiency
Surface and superfinishing also contribute directly to sustainability goals. Components with superior surface quality exhibit lower friction, leading to reduced energy consumption in operation. Longer service life means fewer replacements, conserving raw materials and reducing waste.
Additionally, advancements in finishing technologies are making processes more environmentally responsible. Water-based abrasives, optimized slurry usage, reduced rework, and energy-efficient machines are minimizing the environmental footprint of finishing operations.
From a manufacturing perspective, improved surface finish often enables downsizing of components without compromising performance, contributing to lightweighting initiatives in automotive and aerospace sectors.
Future Trends in Surface and Superfinishing
The future of surface and superfinishing lies in greater process integration, intelligence, and customization. Hybrid machines that combine machining and finishing in a single setup are reducing handling errors and improving efficiency. Advanced abrasive materials and coatings are extending tool life and enabling finer finishes on hard-to-machine materials.
Laser-based surface texturing and finishing technologies are also gaining traction, offering precise control over surface patterns for enhanced tribological performance. Meanwhile, simulation and digital twins are beginning to play a role in predicting surface outcomes and optimizing finishing parameters even before physical trials.
As materials evolve—ranging from advanced alloys and composites to additively manufactured parts—the importance of tailored surface finishing strategies will only increase.
Conclusion: Surface Finish as a Strategic Advantage
Surface and superfinishing are no longer secondary operations relegated to the end of the production line. They are strategic processes that directly influence product performance, reliability, efficiency, and sustainability. In a competitive manufacturing landscape where differentiation increasingly lies in quality and lifecycle value, surface integrity has become a defining parameter.
Manufacturers that recognize and invest in advanced surface and superfinishing capabilities position themselves to deliver superior products, meet stringent industry standards, and achieve long-term operational excellence. Ultimately, in precision manufacturing, it is the surface that tells the final story of engineering intent—and superfinishing ensures that story is one of durability, efficiency, and excellence.
Surface and superfinishing are no longer secondary operations relegated to the end of the production line. They are strategic processes that directly influence product performance, reliability, efficiency, and sustainability. In a competitive manufacturing landscape where differentiation increasingly lies in quality and lifecycle value, surface integrity has become a defining parameter.”